Search info
Search infoWhat Are You Looking For?
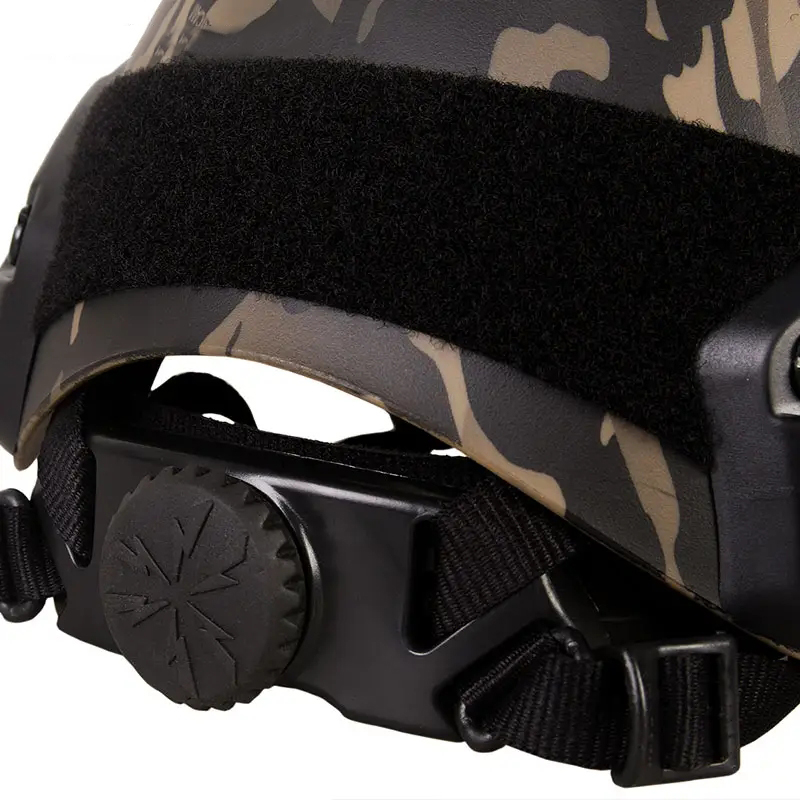
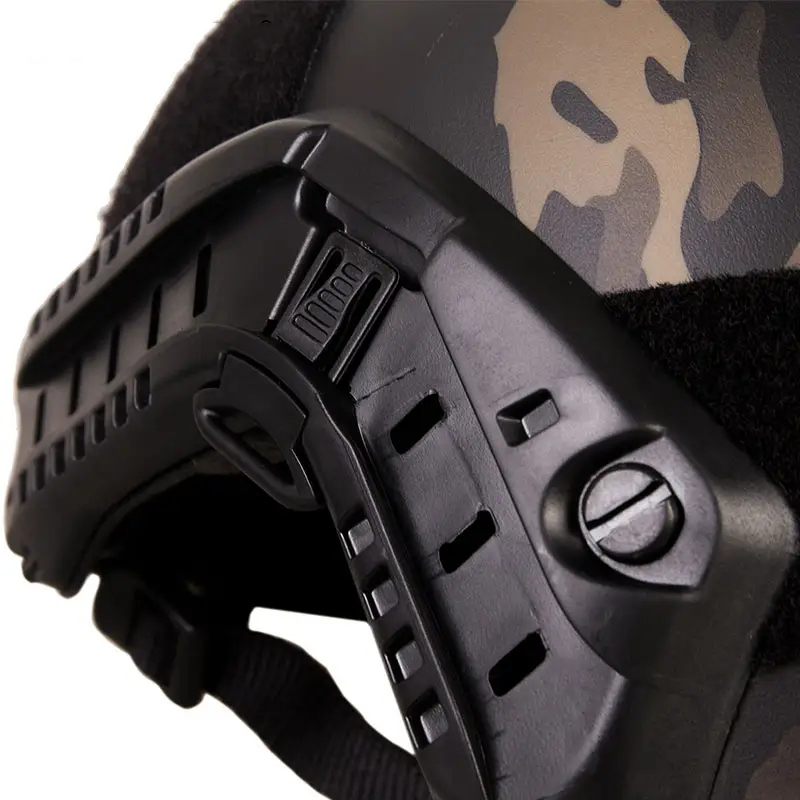
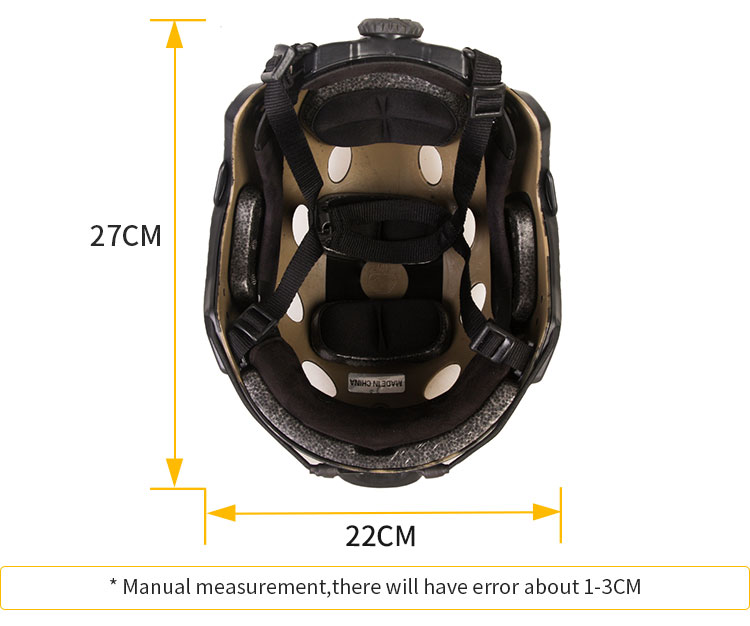
A bulletproof helmet is a single soldier's head protective equipment, mainly used to resist damage to the head from projectiles or fragments. Its core function is to protect the wearer from fatal injuries in the battlefield or high-risk environments. The structure usually consists of a helmet shell, suspension cushioning system and face mask, and is made of advanced materials such as polyethylene, titanium alloy and Kevlar fiber to improve protection while reducing weight; models such as Browning bulletproof helmets also integrate neck protective cape components to optimize wearing comfort and defensive range
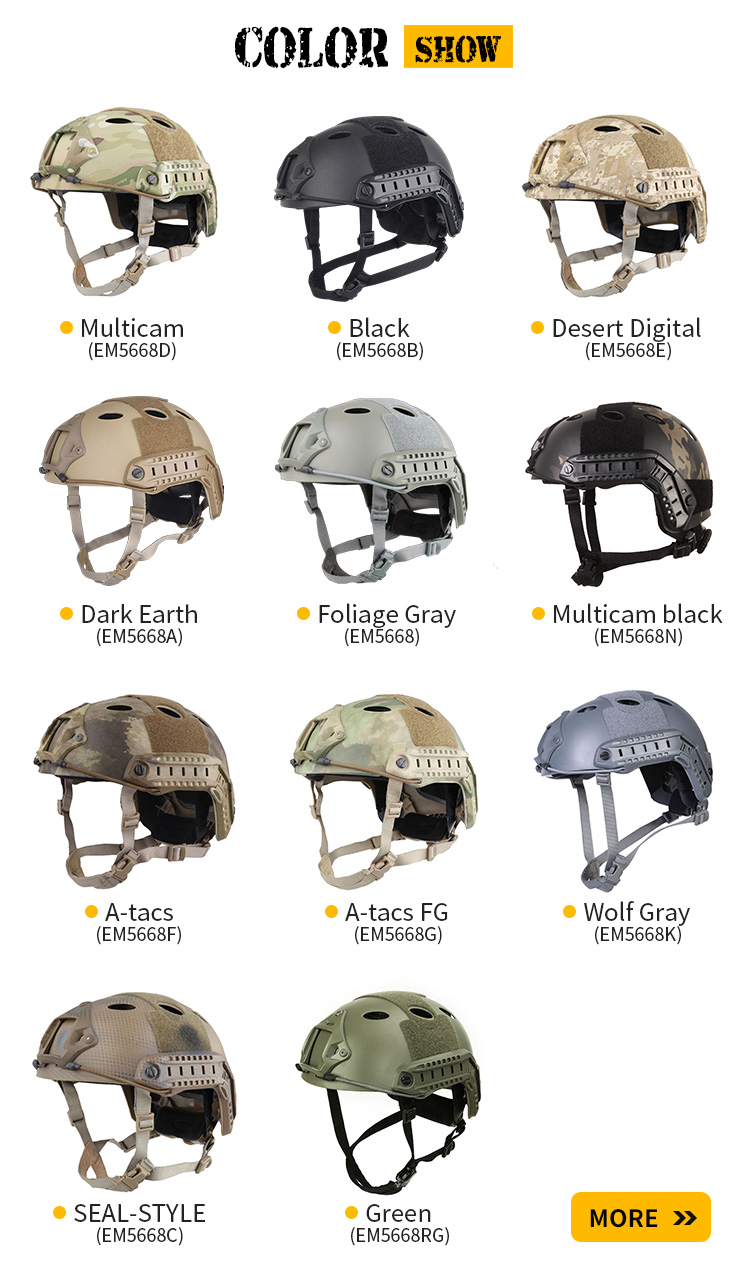
The materials of bulletproof helmets can be divided into three categories according to the helmet shell: metal, non-metal, metal and non-metal composite. Metal materials mainly include steel, aluminum, etc. Helmets made of this material are relatively heavy. Among non-metallic materials, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and aramid are commonly used. Among them, helmets made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber are lighter. For example, a bulletproof helmet that meets the level 2 protection requirements of the Ministry of Public Security's GA293-2012 "Police Bulletproof Helmet and Face Mask" standard weighs only 1.2kg. Non-metallic materials also include ceramic materials, such as chrome steel jade and boron carbide. These ceramic materials have high hardness and impact resistance and can effectively resist attacks by bullets and other high-speed objects. Composite materials are also an important material for making bulletproof helmets. For example, carbon fiber composite materials have high strength and lightweight characteristics. In general, the material selection of bulletproof helmets needs to be determined according to specific usage scenarios and needs to achieve the best protective effect.